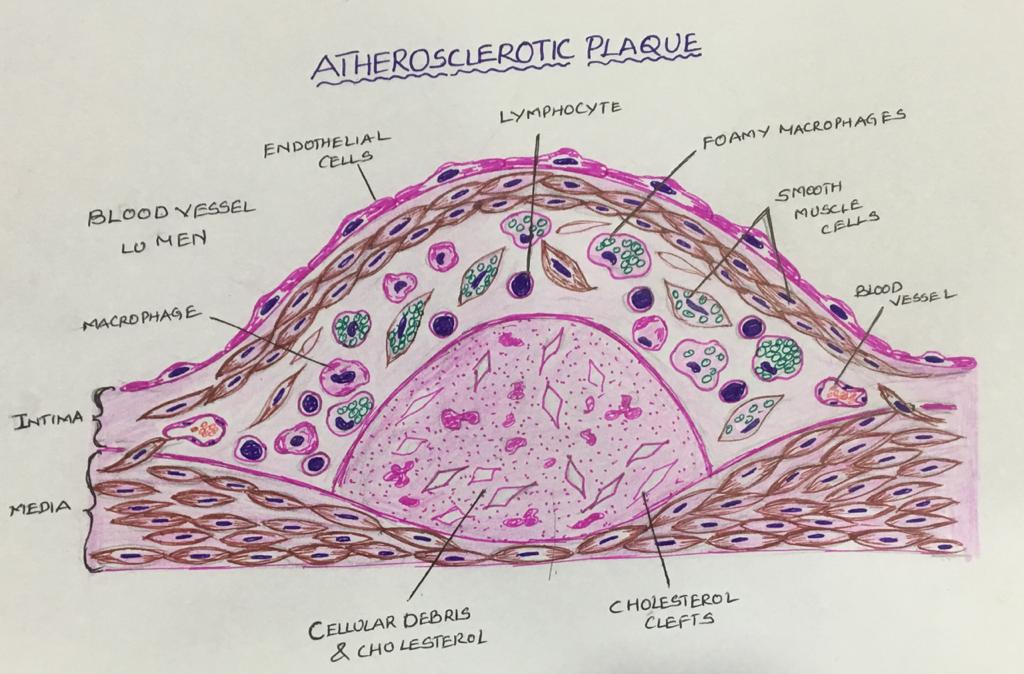
Foam Cell Histopathology . Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques.
from www.histopathology.guru
The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques.
MORPHOLOGY OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS Histopathology.guru
Foam Cell Histopathology The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole.
From www.researchgate.net
—Histopathology of heart on days 2, 3, 5, and 16. F344 controls and Foam Cell Histopathology Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.researchgate.net
Histological findings of esophageal xanthoma. (A) Various sized Foam Cell Histopathology Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From depositphotos.com
Foam cell. Cell structure — Stock Vector © edesignua 193985012 Foam Cell Histopathology A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From pathologia.ed.ac.uk
Atherosclerosis and atheroma Pathologia Foam Cell Histopathology The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Foam cells play an important role. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From basicmedicalkey.com
NiemannPick Disease Basicmedical Key Foam Cell Histopathology A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. As a major component of atherosclerotic. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From morancore.utah.edu
Moran CORE Cellular Histopathology Foam Cell Histopathology As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. Foam cells play an important role at all. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From mavink.com
Fibrous Histiocytoma Foam Cell Histopathology The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. Foam cells play an important role. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.researchgate.net
Progressive atherosclerotic lesions. Pathological intima thickening Foam Cell Histopathology Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.researchgate.net
Histopathological slide of an oral squamous cell carcinoma showing Foam Cell Histopathology A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From en.m.wikipedia.org
FileGallbladder adenocarcinoma (2) histopathology.jpg Wikipedia Foam Cell Histopathology Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From imagebank.hematology.org
Figure 03 Bone marrow aspirate showing macrophage with abundant Foam Cell Histopathology Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Foam cells undergo. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.researchgate.net
Foam cells are present in the papillary dermis (H and E X 400 Foam Cell Histopathology Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From ijdvl.com
Histoid leprosy presenting with figurate lesions A unique and rare Foam Cell Histopathology As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. A foam cell is any cell that has. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.cell.com
Foam Cells One Size Doesn’t Fit All Trends in Immunology Foam Cell Histopathology Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. A foam cell is any cell that has. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.reddit.com
Help me look at this histology Which ones are the "inflammatory Foam Cell Histopathology Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques. The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Massive intracellular lipid. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.researchgate.net
Boa imperator skin histopathology using Toluidine blue staining. The Foam Cell Histopathology A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Foam cells undergo diverse pathways of programmed cell death including apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.pathologyoutlines.com
Pathology Outlines Xanthoma Foam Cell Histopathology A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Massive intracellular lipid accumulation causing the formation of foam cells results from the enhanced modified low. As a major component of atherosclerotic plaques, foam cells contribute to cholesterol deposition and plaques growth (. The results of this study showed that the. Foam Cell Histopathology.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 1 from Presence of Foam Cells in Kidney Interstitium Is Foam Cell Histopathology The results of this study showed that the differential genes mainly regulated the transformation of macrophages into foam cells. Foam cells play an important role at all stages of atherosclerotic lesion development, from initial lesions to advanced plaques. A foam cell is any cell that has ingested lipids, thus giving the histologic appearance of a sudsy vacuole. Massive intracellular lipid. Foam Cell Histopathology.